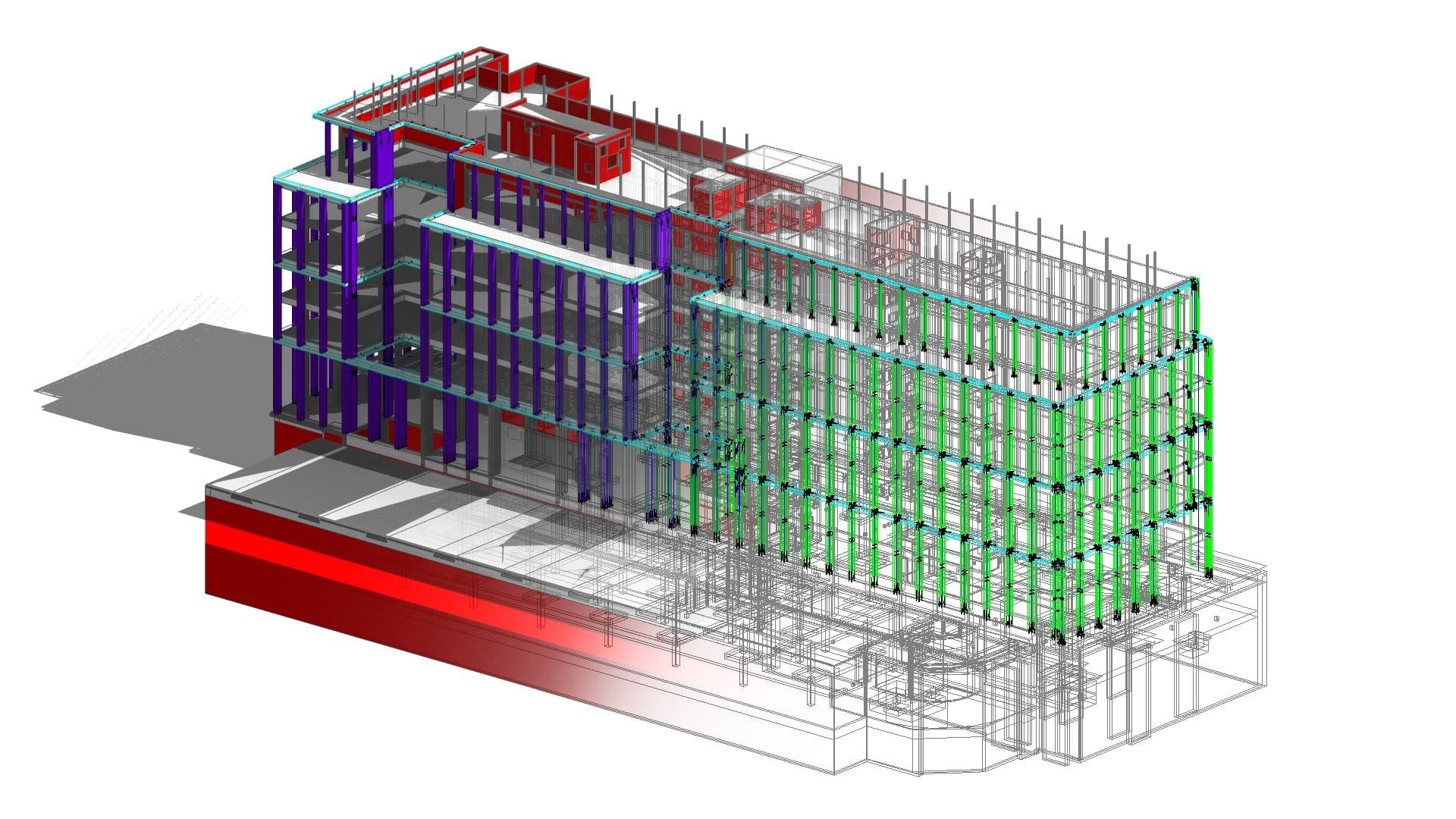
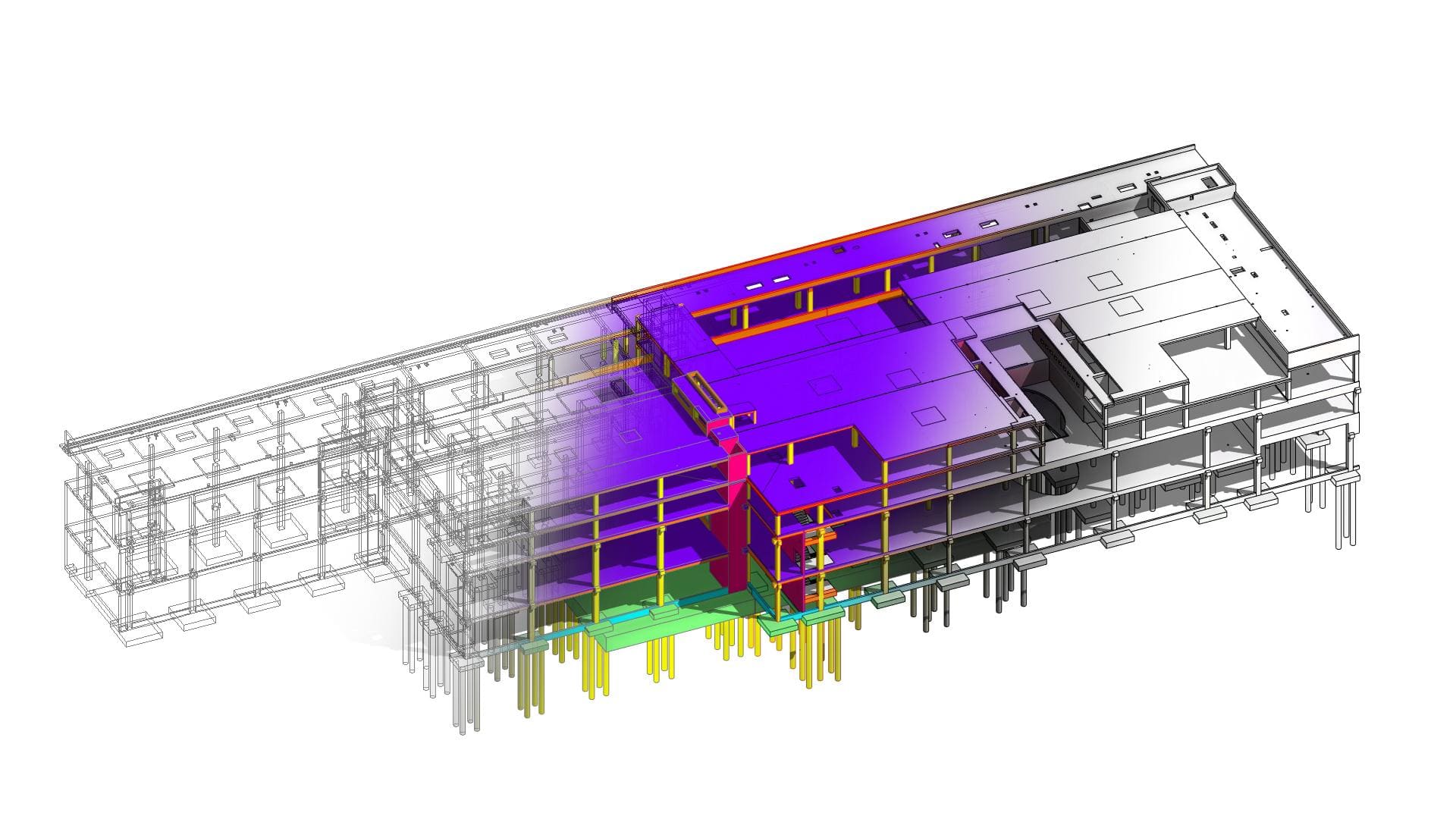
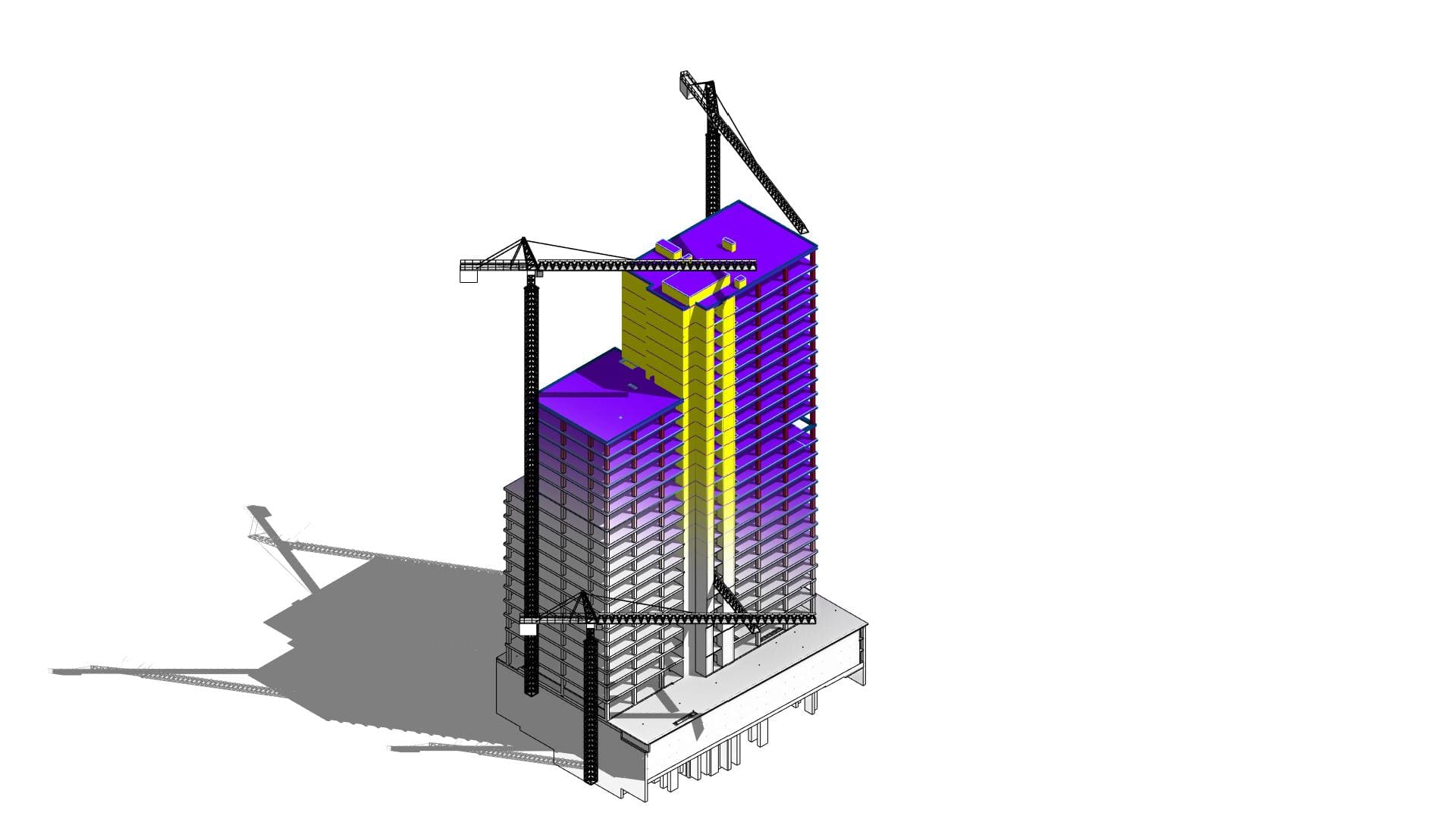
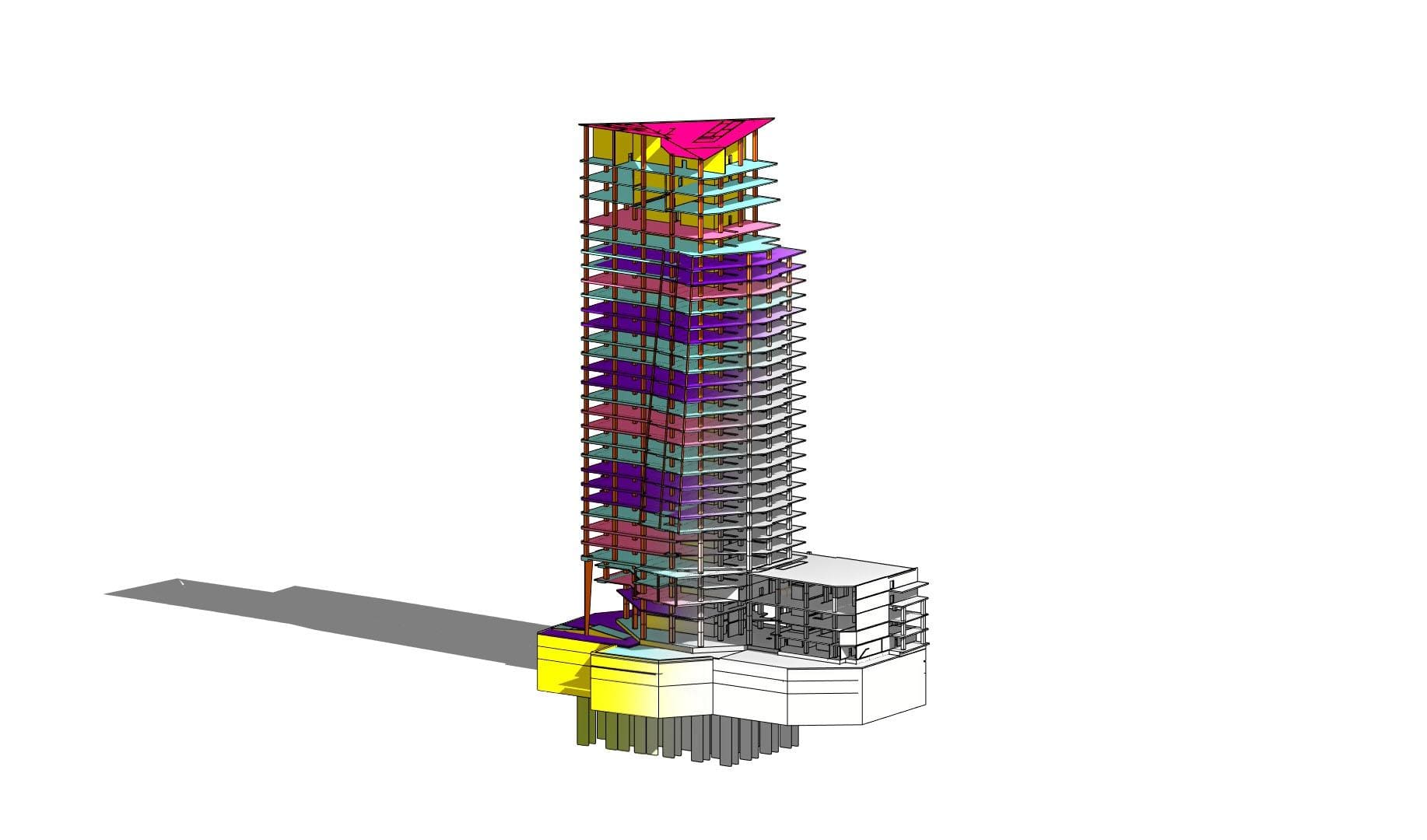
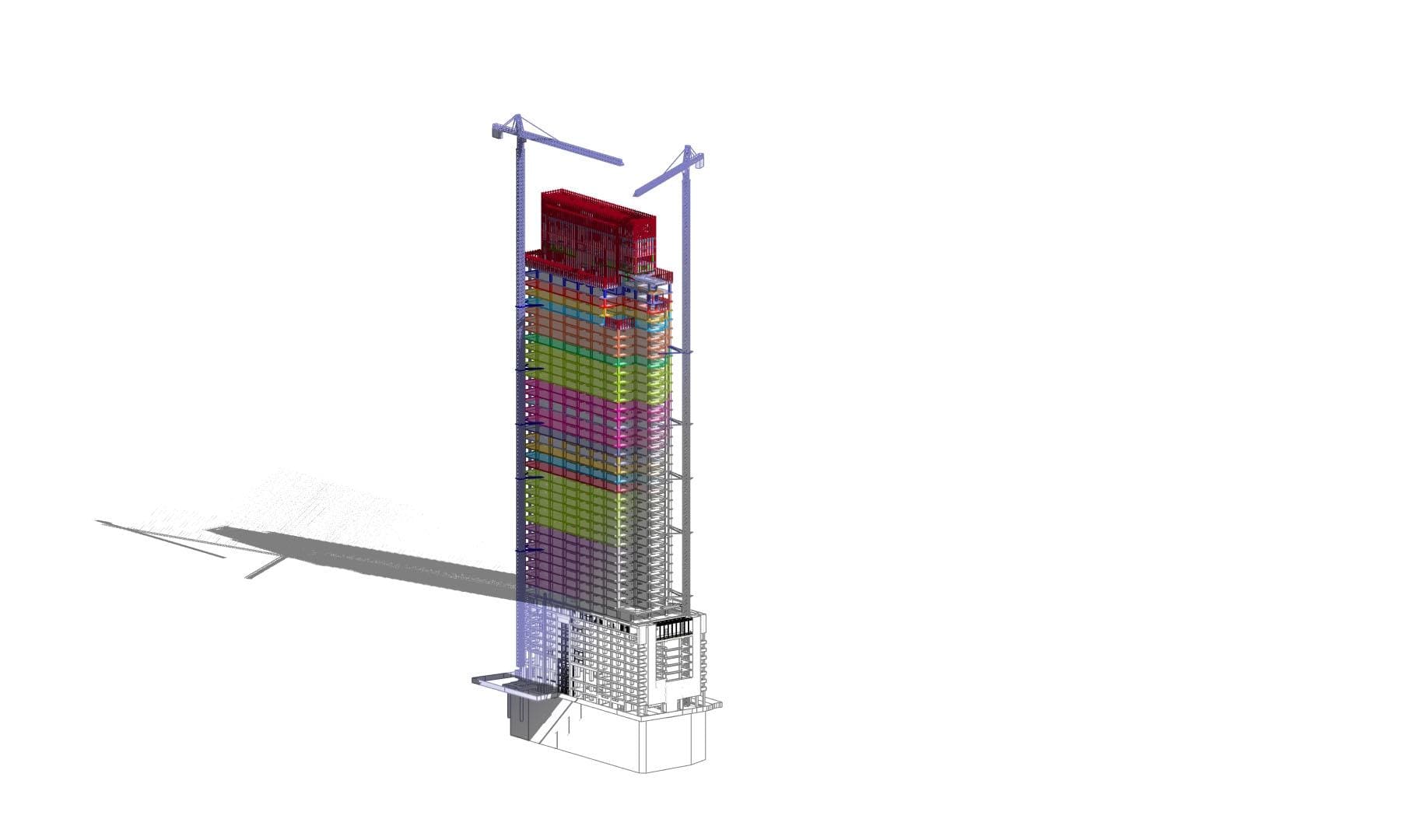
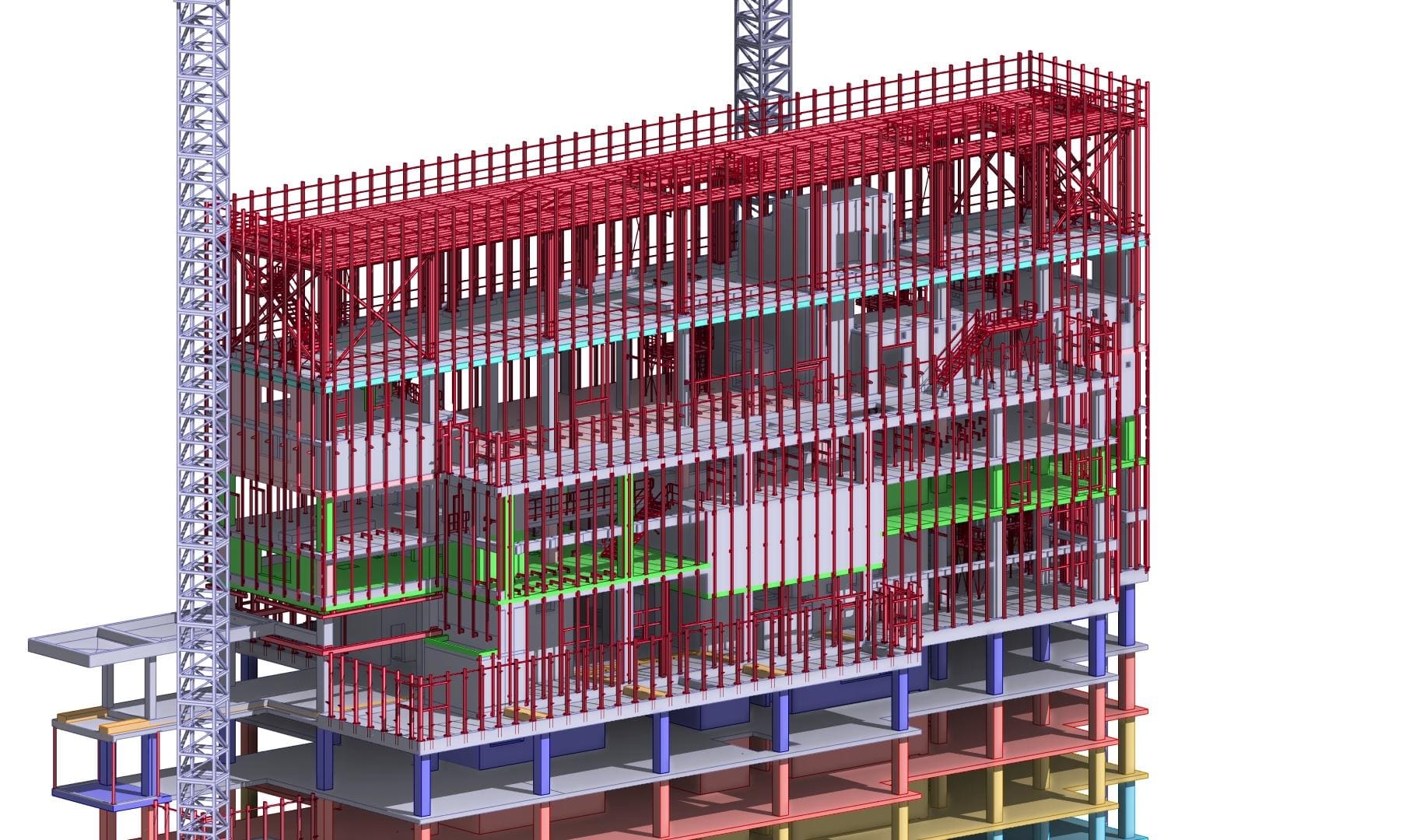
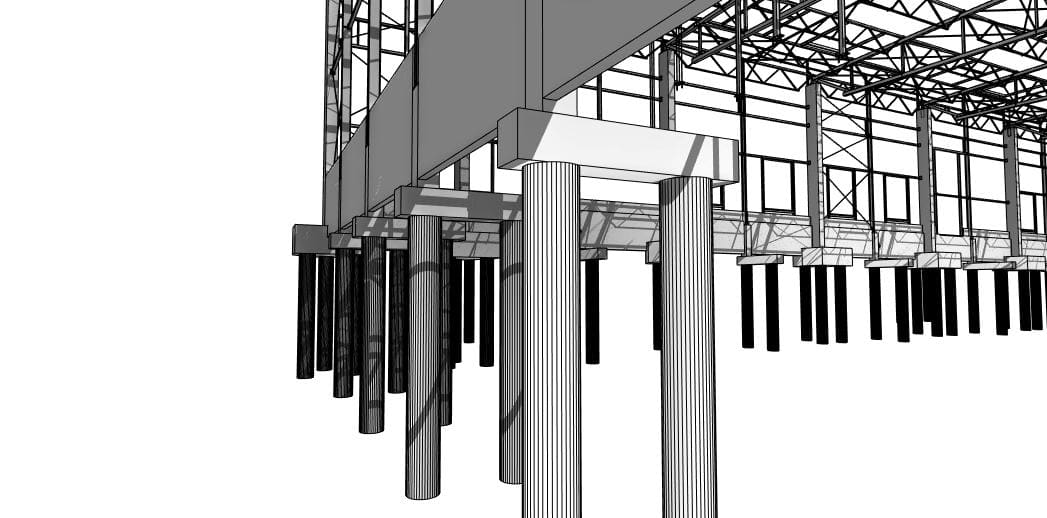
Looking most generally at the concept of BIM, it can be said that it is a methodology related to both parametric modeling of information about a building object and the management of this information in relation to the entire life cycle of this object.
The BIM environment gives us endless possibilities of both modeling and information management. This information may have a graphic or non-graphical dimension, and this differentiation allows us to explain what a 3D BIM model really is. So the 3D model saturated with multidimensional standardized information makes us start operating in the BIM world. Creating a “digital twin” of a real object, reflecting not only its geometric features, but also properties and their mutual relations, opens the door to wide possibilities of activities in the field of each design stage.
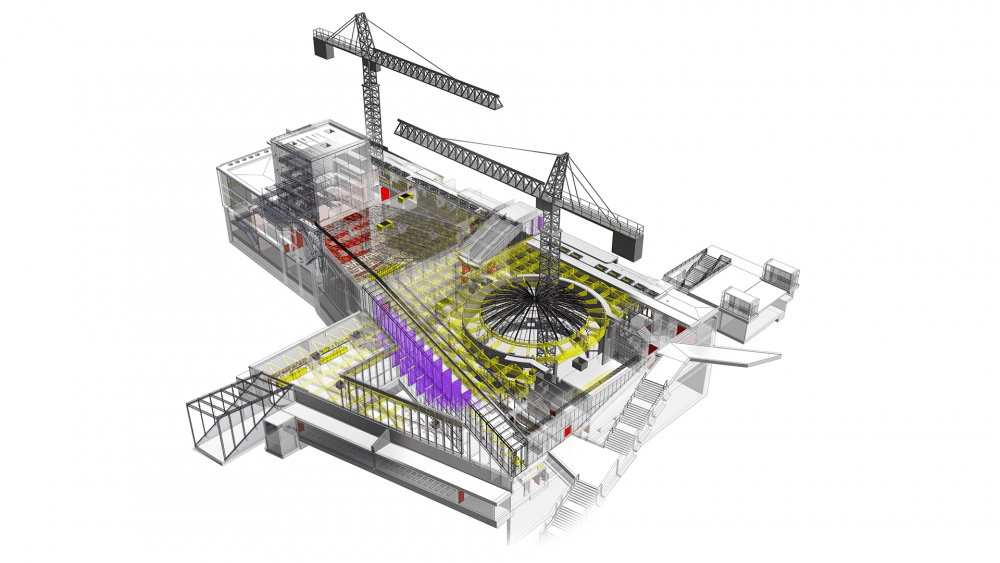
Polish Theater. Szczecin
The unquestionable advantage of BIM is its multidimensionality. The multitude of data in which we can supplement our 3D BIM model means that we enter the next dimensions of 4D, 5D … 7D, and presumably, taking into account the development of technology, it will not end there. The model, enriched with information on the schedule, costs, environmental impact of the facility, etc., is invaluable in terms of the complexity of information provided in the design process, both at the design stage, at the execution stage and during facility maintenance. This makes it possible to carry out a series of complex but binding analyzes already at the concept stage. Such a model can also be used as a basis for creating cost estimates or help in planning a construction site, and it is impossible to list the entire range of possibilities here. On the other hand, the spatial visualization of solutions alone makes it possible to show the results of our work in a more understandable way to people who are not particularly close to engineering.
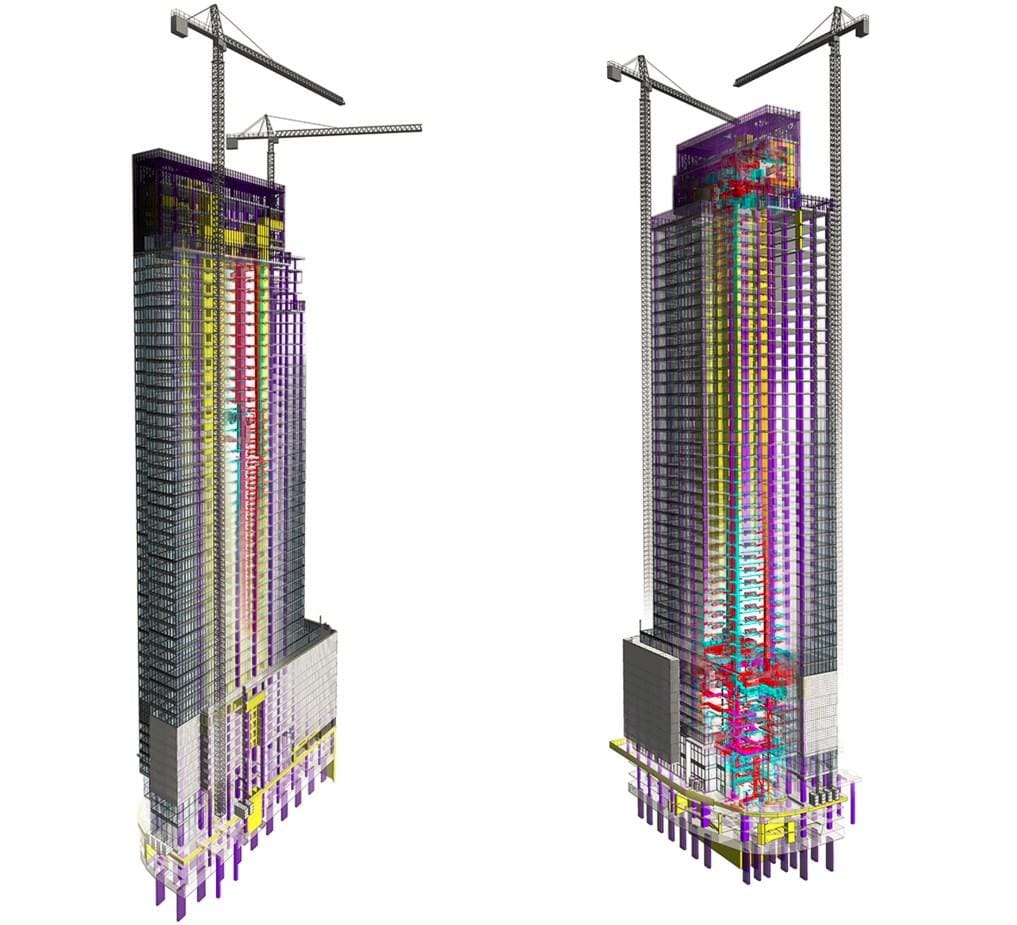
UNIT high-rise building. Warsaw
Because we know how important an issue is inter-industry cooperation, we pay special attention to the interdisciplinary nature of BIM. Working on the basis of an integrated model gives you a direct opportunity to manage information from various industries. Cross-industry coordination carried out at the level of BIM models maximally streamlines and optimizes coordination processes. This feature is particularly important as it allows for the detection of inter-industry collisions at an early stage, which significantly speeds up the design process, and also reduces the number of errors detected directly on the construction site, thus minimizing costs.
BIM supports technological neutrality and enables interoperability. Open formats, such as the IFC format, enable the exchange of information between teams working on different software. Thanks to this, multi-discipline teams can work together without changing their platforming habits. Additionally, basing the process on common CDE data environments creates a transparent and unambiguous process in terms of the flow of information and responsibility for the introduced changes.
BIM has revolutionized the approach to design, as well as to all other phases related to the entire life cycle of the facility. Thus, it influenced the internal change in the work of a design office such as ours, as well as its cooperation with other project participants, as well as the Investor. It has built up our awareness of how advanced the final product of our work can be, and this is what we try to pass on to our clients.
Below are examples of BIM projects in which we have participated:
- Commercial building. Warsaw
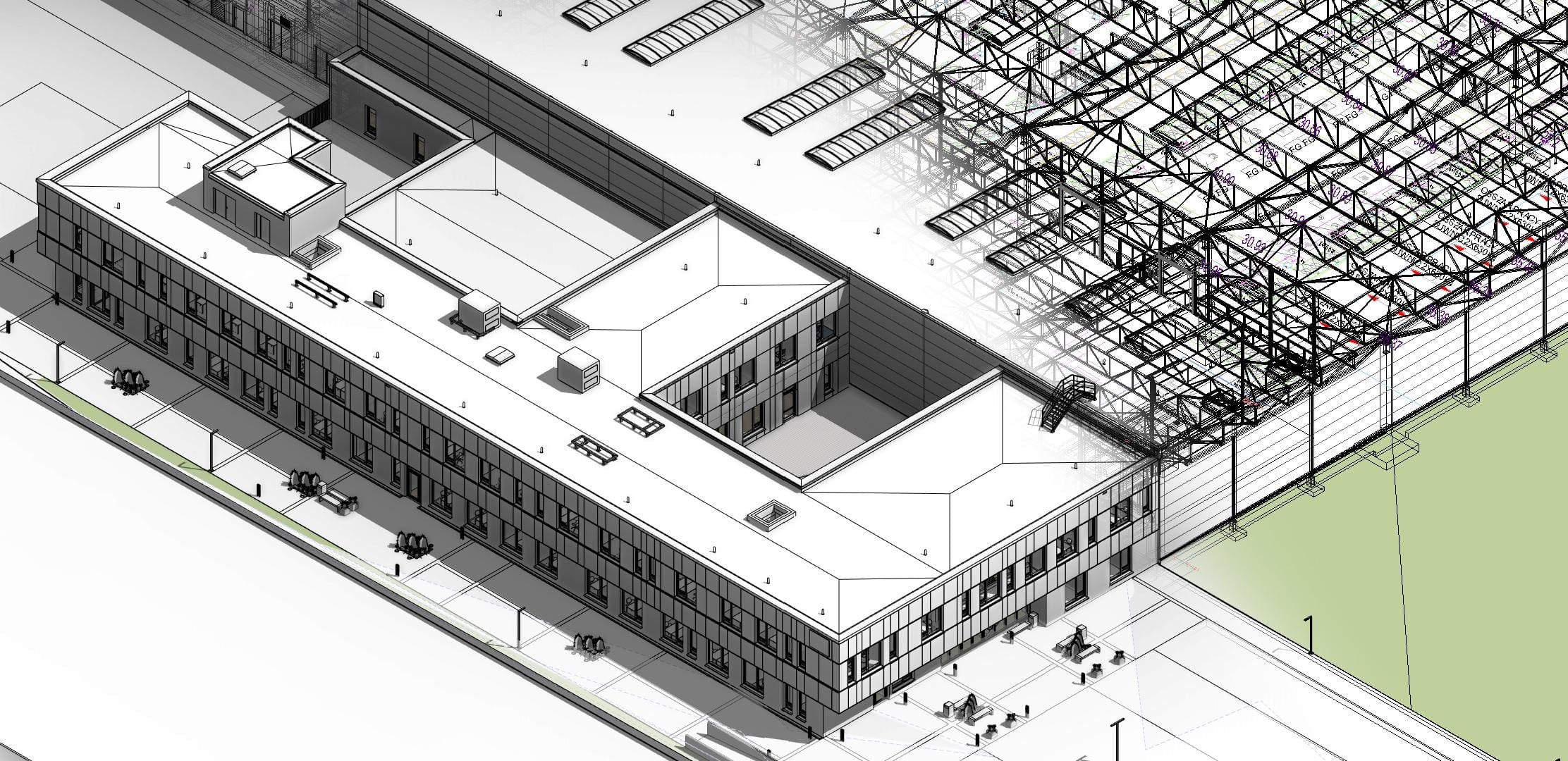
- Public building
- Shopping center. Warsaw
- Commercial building
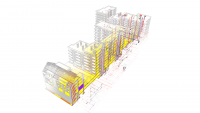
- High-rise building
- High-rise building
- High-rise building
- Commercial building
- Residential. Gdańsk
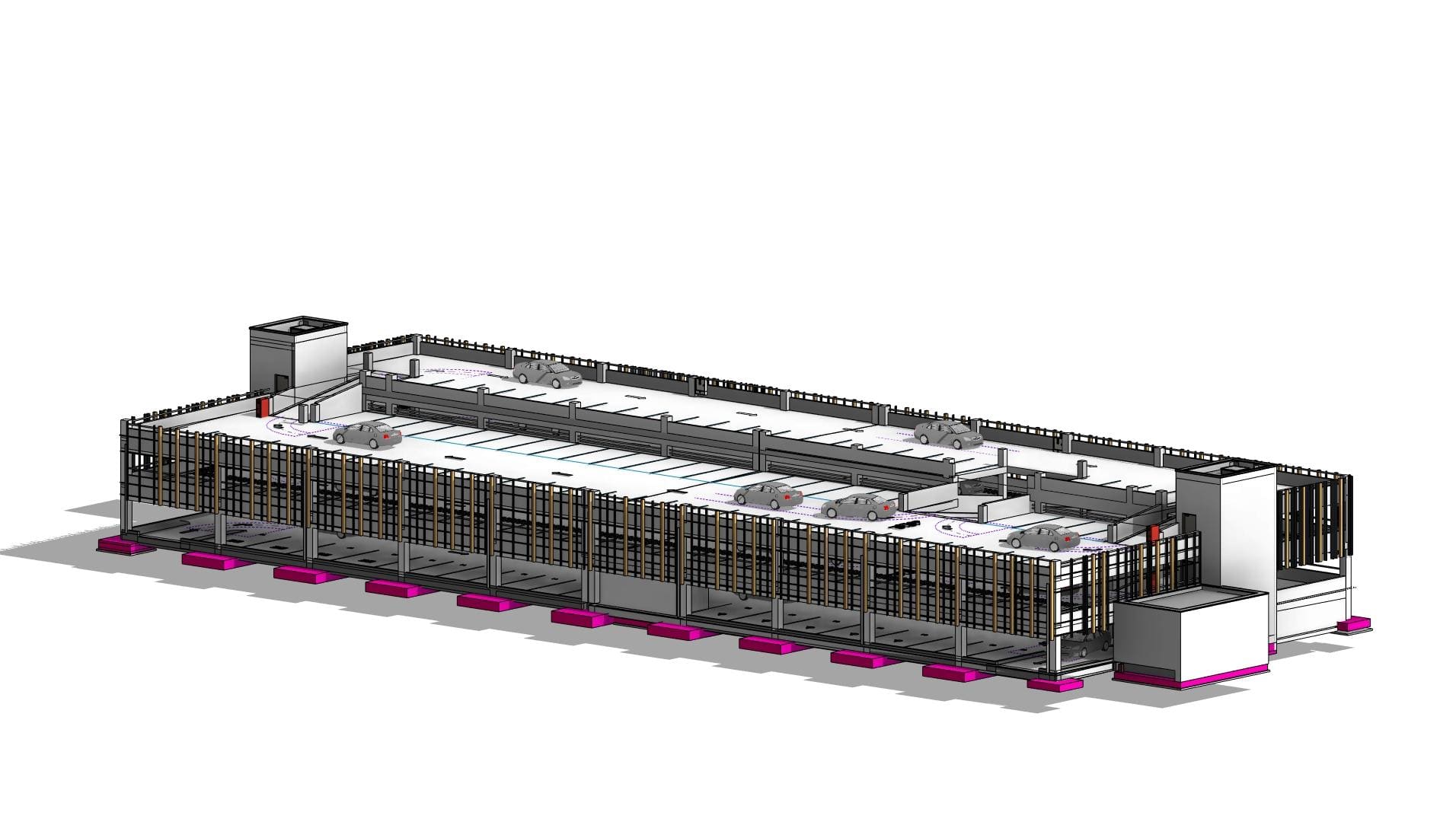
- Parking. Toruń
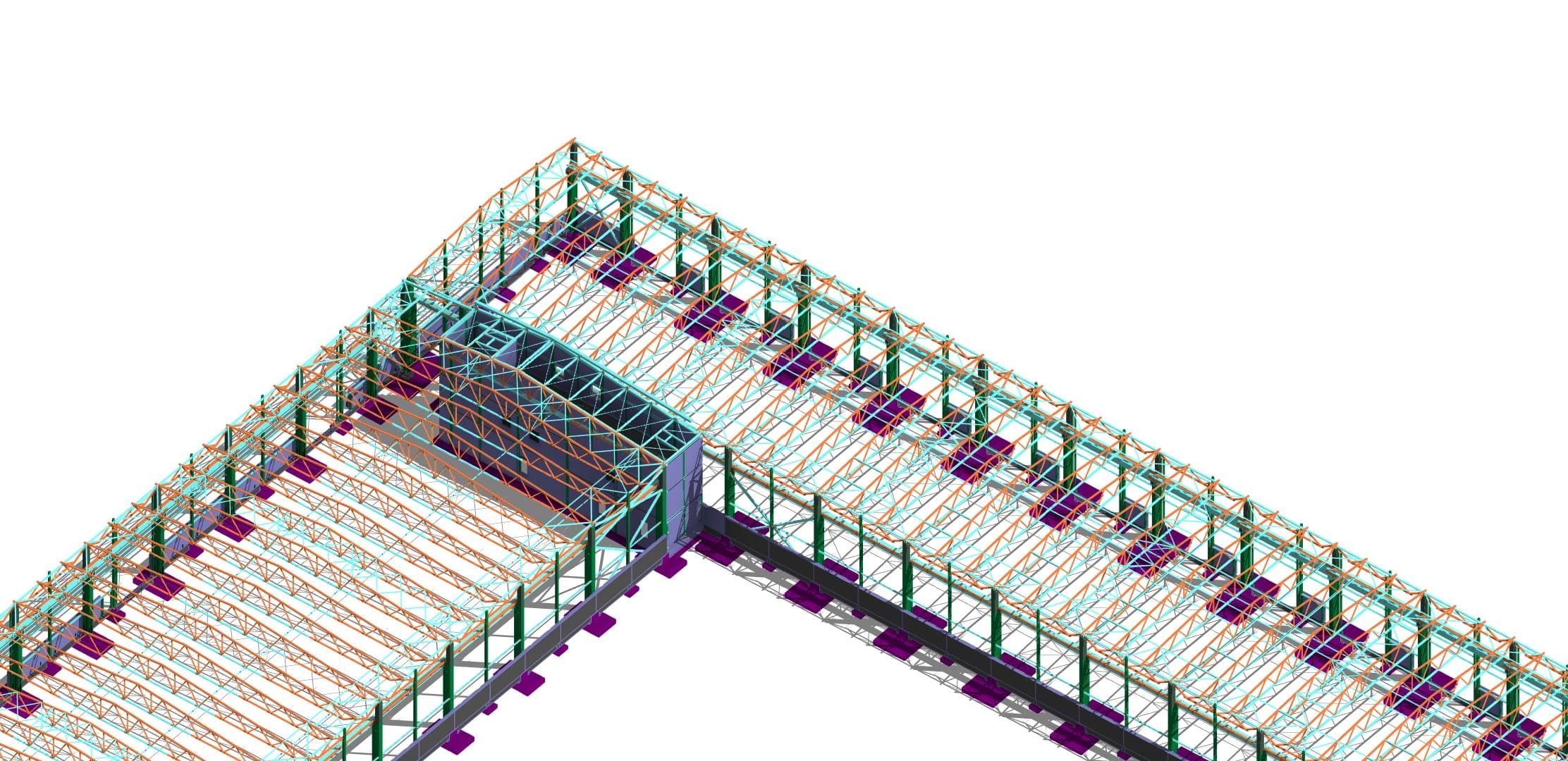
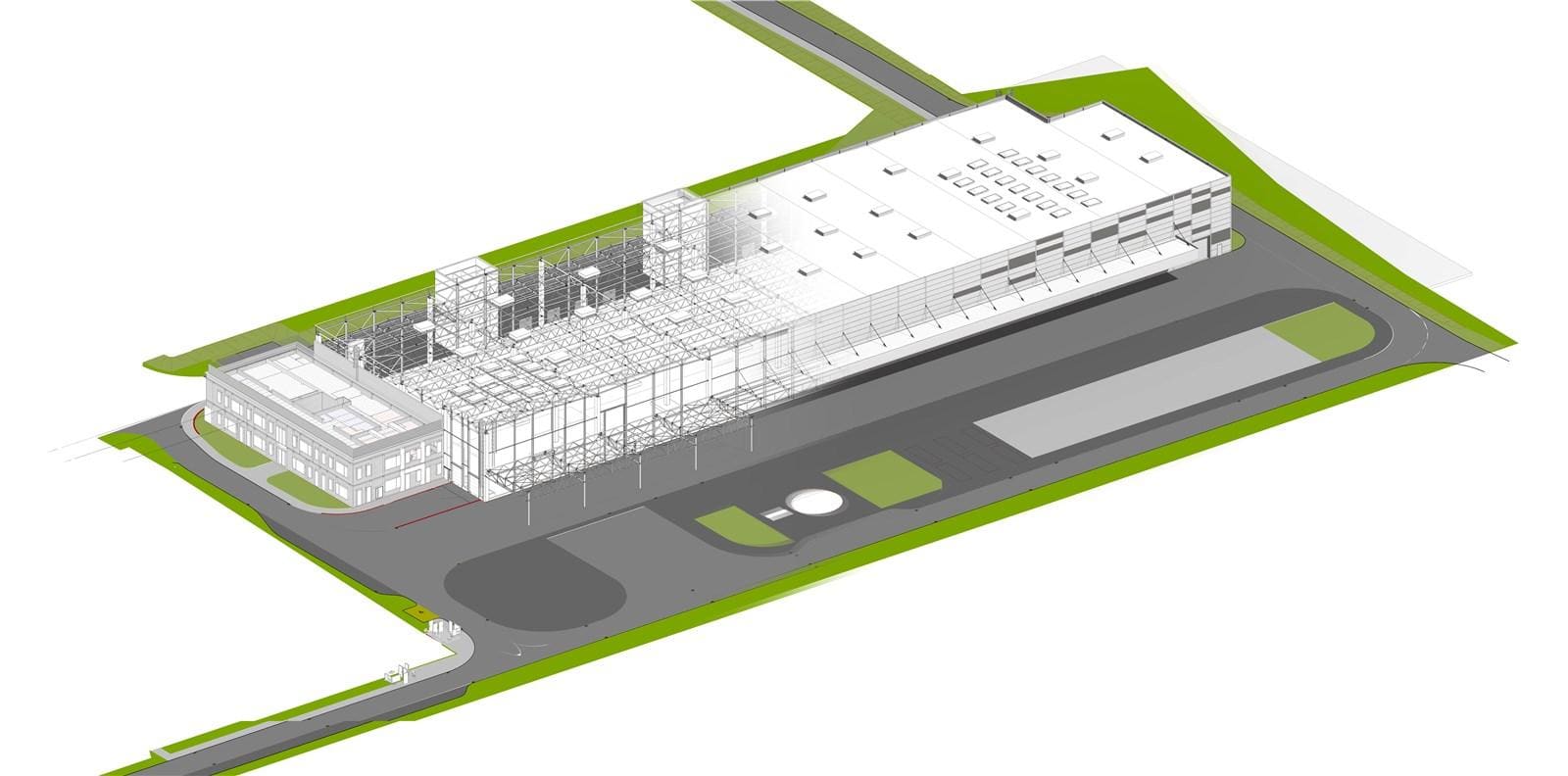
- Production facility. Bydgoszcz
- Production facility. Gdynia
- Production facility. Toruń
- Warehouse. Gdańsk
- Production facility. Poznań